Artekit PropBoard: Motion API
Motion API documentation for the Artekit PropBoard.
Motion API
Motion sensing in the PropBoard is managed through the Motion object.
class PropMotion;
PropMotion Motion;
The Motion object is already instantiated when the program begins, and has to be initialized with the Motion.begin function. After that, you can configure and use most features of the MMA8452Q sensor through the API functions.
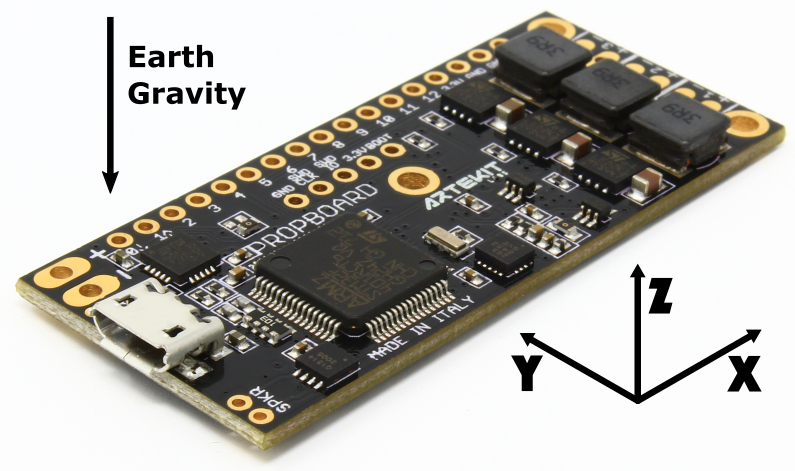
Sensor orientation
Interrupt handling
The Motion object wraps most of the MMA8452Q 3-Axis accelerometer functionality. The MMA8452Q accelerometer is capable of detecting certain motion events using its internal DSP processor and can generate interrupts when these events are detected. This way the PropBoard processor is free from the task of polling the accelerometer asking for new event data. The Motion object supports the “Data Ready”, “Any Motion”, “Single Pulse”, and “Transient” events.
The MMA8452Q can map any of these events into 2 interrupt signals. Whenever you configure an event through the Motion.configDataReady, Motion.configAnyMotion, Motion.configTransient and Motion.configPulse functions, you will be presented with an option to map a given event to either MotionInterrupt1 or MotionInterrupt2 signals. It’s up to you to decide which event to map on which signal.
Then you can configure a function to be called whenever one of these two interrupts are signaled. The Motion.attachInterrupt function allows you to attach a signal to a function you define, much like Arduino’s attachInterrupt function does with interrupts on a pin.
For example, the code below uses the Motion.configPulse function to configure the “Pulse” event and to map the event to the MotionInterrupt1 signal. Then, the Motion.attachInterrupt attachs the MotionInterrupt1 signal to the pulseDetected function to be called when the event is detected.
volatile bool on_pulse = false;
void setup()
{
// Initialize motion sensor
Motion.begin();
// Configure serial
Serial.begin(9600);
// Configure pulse and map event to MotionInterrupt1
Motion.configPulse(AxisAll, 3.78f, 500, 100, MotionInterrupt1);
// Attach MotionInterrupt1 to the pulseDetected function
Motion.attachInterrupt(MotionInterrupt1, pulseDetected);
}
void loop()
{
// The on_pulse variable is set in the pulseDetected function
if (on_pulse)
{
// Pulse detected, reset variable
on_pulse = false;
// and write a message
Serial.println("Pulse detected !");
// Do other motion processing here
}
}
void pulseDetected()
{
// The motion sensor signals that a pulse event was detected
on_pulse = true;
}
This event-signal mapping is the recommended way to work with the motion sensor. It is also recommended not to call Motion API functions inside interrupt handlers (the pulseDetected function in the above example): set a variable that you then evaluate from the loop function instead and do the required motion processing outside the interrupt context.
If no interrupt is configured for a given event, you can still detect the event by polling using the following functions: Motion.getAnyMotionSource for “Any Motion” event, Motion.getTransientSource for “Transient” event and Motion.getPulseSource() for “Pulse event.
Motion.begin
Call the Motion.begin function to initialize the motion sensor.
Syntax
bool begin(uint8_t scale = 8, uint16_t odr = 200, bool enable = true);
Parameters
The scale parameter is the sensor scale in g’s and can be one of the following values:
- 2
- 4
- 8
The odr parameter is the output data rate. It sets how many samples per second the sensor will output. The lower the frequency, the higher the precision. It can be one of the following values:
- 1
- 6
- 12
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 400
- 800
The enable parameter is used to automatically enable the sensor after the initial configuration. If true the sensor is enabled; if false the sensor remains disabled until the Motion.enable function is called.
If no parameters are provided, the Motion object is initialized and enabled with scale = 8 and output data rate = 200.
Returns
Returns true on success, false otherwise.
Examples
The following code shows the standard initialization.
void setup()
{
Motion.begin();
}
The code here below shows a custom initialization with scale = 4 and output data rate = 800.
void setup()
{
// Configure the motion sensor with scale = 4 and output data rate = 800
Motion.begin(4, 800, false);
// Do other Motion configuration and then enable the motion sensor
// ...
Motion.enable();
}
Motion.end
Call the Motion.end function to disable the motion sensor and de-initialize the Motion object.
Syntax
void end();
Parameters
None.
Returns
None.
Motion.enable
Call the Motion.enable function to enable the motion sensor.
Syntax
bool enable();
Parameters
None.
Returns
Returns true on success, false otherwise.
Motion.disable
Call the Motion.disable function to disable the motion sensor.
Syntax
bool disable();
Parameters
None.
Returns
Returns true on success, false otherwise.
Motion.setScale
Call the Motion.setScale function to change the scale after the motion sensor has been initialized with the Motion.begin function.
Syntax
bool setScale(uint32_t scale);
Parameters
The scale parameter is the sensor scale in G and can be one of the following values: * 2 * 4 * 8
Returns
Returns true on success, false otherwise.
Motion.setDataRate
Use the Motion.setDataRate function to change the output data rate after the motion sensor has been initialized with the Motion.begin function.
Syntax
bool setDataRate(uint32_t data_rate);
Parameters
The data_rate parameter is the output data rate. It sets how many samples per second the sensor will output. The lower the frequency, the higher the precision. It can be one of the following values:
- 1
- 6
- 12
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 400
- 800
Returns
Returns true on success, false otherwise.
Motion.configDataReady
Configures the interrupt number to be used when a “Data Ready” event is generated from the motion sensor.
Syntax
bool configDataReady(MotionInterrupt irq);
Parameters
The irq parameter is the interrupt number to use and can be one of the following values:
- MotionInterruptNone: disables the interrupt generation
- MotionInterrupt1: use interrupt number 1
- MotionInterrupt2: use interrupt number 2
Returns
Returns true on success, false otherwise.
See also
Motion.configAnyMotion
Use this function to configure the “Any Motion” event detection. The “Any Motion” event is an acceleration greater than force_mg parameter with a duration longer than time milliseconds.
Syntax
bool configAnyMotion(Axis axis, float force_mg, uint32_t time, MotionInterrupt irq = MotionInterruptNone);
Parameters
The axis parameter configures on which axis the event will be detected. Can be a combination of any of the following values:
- AxisX: event detection enabled on X axis.
- AxisY: event detection enabled on Y axis.
- AxisZ: event detection enabled on Z axis.
- AxisAll: event detection enabled on all axis.
The force_mg parameter is the required force in g’s to detect an “Any Motion” event.
The time parameter is the time in milliseconds that the acceleration has to be over force_mg for the event to become valid.
The irq parameter is the interrupt signal number for the event. It can be one of the following values:
- MotionInterruptNone: no interrupt signal is used. The event detection has to be polled with the
Motion.getAnyMotionSourcefunction. - MotionInterrupt1: event is signaled through interrupt 1.
- MotionInterrupt2: event is signaled through interrupt 2.
Returns
Returns true on success, false otherwise.
Notes
This function will enable the “High Resolution” feature of the MMA8452Q.
Example
volatile bool on_motion = false;
void setup()
{
// Initialize motion sensor
Motion.begin();
// Configure serial
Serial.begin(9600);
// Configure "Any Motion" and map event to MotionInterrupt1.
// Set to 1G during 500ms.
Motion.configAnyMotion(AxisAll, 1, 500, MotionInterrupt1);
// Attach MotionInterrupt1 to the motionDetected function
Motion.attachInterrupt(MotionInterrupt1, motionDetected);
}
void loop()
{
// The on_motion variable is set in the motionDetected function
if (on_motion)
{
// Motion detected, reset variable
on_motion = false;
// and write a message
Serial.println("Motion detected !");
// Do other motion processing here
}
}
void motionDetected()
{
// The motion sensor signals that a motion event was detected
on_motion = true;
}
See also
Motion.configTransient
This function configures the “Transient” event. The “Transient” detection enables a high-pass filter to detect an acceleration on an axis that exceeds a set threshold excluding static acceleration. Much like the “Any Motion” event but able to better detect acceleration changes disregarding initial static acceleration.
Syntax
bool configTransient(Axis axis, float force_mg, uint32_t time, MotionInterrupt irq = MotionInterruptNone);
Parameters
The axis parameter configures on which axis the event will be detected. Can be a combination of any of the following values:
- AxisX: event detection enabled on X axis.
- AxisY: event detection enabled on Y axis.
- AxisZ: event detection enabled on Z axis.
- AxisAll: event detection enabled on all axis.
The force_mg parameter is the required force in g’s to detect an “Any Motion” event.
The time parameter is the time in milliseconds that the acceleration has to be over force_mg for the event to become valid.
The irq parameter is the interrupt signal number for the event. It can be one of the following values:
- MotionInterruptNone: no interrupt signal is used. The event detection has to be polled with the
Motion.getTransientSourcefunction. - MotionInterrupt1: event is signaled through interrupt 1.
- MotionInterrupt2: event is signaled through interrupt 2.
Returns
Returns true on success, false otherwise.
Notes
This function will enable the “High Resolution”, “High pass filter” and “High pass filter cutoff” feature of the MMA8452Q.
Example
volatile bool on_transient = false;
void setup()
{
// Initialize motion sensor
Motion.begin();
// Configure serial
Serial.begin(9600);
// Configure "Transient" and map event to MotionInterrupt1.
// Set to 0.5G during 100ms.
Motion.configTransient(AxisAll, 0.5f, 100, MotionInterrupt1);
// Attach MotionInterrupt1 to the pulseDetected function
Motion.attachInterrupt(MotionInterrupt1, transientDetected);
}
void loop()
{
// The on_transient variable is set in the transientDetected function
if (on_transient)
{
// Pulse detected, reset variable
on_transient = false;
// and write a message
Serial.println("Transient detected !");
// Do other motion processing here
}
}
void transientDetected()
{
// The motion sensor signals that a transient event was detected
on_transient = true;
}
See also
Motion.configPulse
This function configures the “Pulse” detection event. A “Pulse” is a quick positive acceleration followed by a negative acceleration.
Syntax
bool configPulse(Axis axis, float force_mg, uint32_t time, uint32_t latency, MotionInterrupt irq = MotionInterruptNone);
Parameters
The axis parameter configures on which axis the event will be detected. Can be a combination of any of the following values:
- AxisX: event detection enabled on X axis.
- AxisY: event detection enabled on Y axis.
- AxisZ: event detection enabled on Z axis.
- AxisAll: event detection enabled on all axis.
The force_mg parameter is the required force in G to detect an “Any Motion” event.
The time parameter is the time in milliseconds the motion has to be over force_mg for the event to become valid.
The latency parameter is the minimum time in milliseconds that has to pass before considering any other “Pulse” event. “Pulse” events during this period will be ignored.
The irq parameter is the interrupt signal number for the event. It can be one of the following values:
- MotionInterruptNone: no interrupt signal is used. The event detection has to be polled with the
getTransientSourcefunction. - MotionInterrupt1: event is signaled through interrupt 1.
- MotionInterrupt2: event is signaled through interrupt 2.
Returns
Returns true on success, false otherwise.
Example
See example for Interrupt handling.
Motion.attachInterrupt
Use this function to attach a motion sensor interrupt to a user-defined function.
Syntax
bool attachInterrupt(MotionInterrupt irq, MotionInterruptCallback* callback);
Parameters
The irq parameter is the motion sensor interrupt. Can be one of the following values:
- MotionInterrupt1
- MotionInterrupt2
The callback parameter is a pointer to a function defined as void function_name(), where function_name can be any name.
Returns
Returns true on success, false otherwise.
Example
See example for Interrupt handling.
Motion.getInterruptSource
Call this function to read from the motion sensor the interrupt source. Useful when multiple events are attached to a single interrupt signal.
Syntax
MotionEvent getInterruptSource();
Parameters
None.
Returns
The function can return a combination of the following values:
- MotionEventNone: No events were detected
- MotionEventDataReady: A “Data Ready” event was detected. The event has to be cleared by reading the X, Y, Z values with the
Motion.read (g)orMotion.read (raw)functions. - MotionEventAnyMotion: An “Any Motion” event was detected. The event has to be cleared by calling the
Motion.getAnyMotionSource()function. - MotionEventPulse: A “Pulse” event was detected. The event has to be cleared by calling the
Motion.getPulseSourcefunction. - MotionEventTransient: A “Transient” event was detected. The event has to be cleared by calling the
Motion.getTransientSourcefunction.
Example
volatile bool on_interrupt = false;
void setup()
{
Motion.begin();
// Configure "Any Motion" and map event to MotionInterrupt1.
// Set to 1G during 500ms.
Motion.configAnyMotion(AxisAll, 1, 500, MotionInterrupt1);
// Configure "Transient" and map event to MotionInterrupt1.
// Set to 0.5G during 100ms.
Motion.configTransient(AxisAll, 0.5f, 100, MotionInterrupt1);
// Attach MotionInterrupt1 to the pulseDetected function
Motion.attachInterrupt(MotionInterrupt1, myInterruptHandler);
}
void loop()
{
uint8_t event;
uint8_t source;
if (on_interrupt)
{
event = Motion.getInterruptSource();
if (event & MotionEventAnyMotion)
{
// Any motion detected
source = Motion.getAnyMotionSource();
// ... Process 'source' ...
}
if (event & MotionEventTransient)
{
// Transient detected
source = Motion.getTransientSource();
// ... Process 'source' ...
}
}
}
void myInterruptHandler()
{
// Signal on_interrupt
on_interrupt = true;
}
Motion.getAnyMotionSource()
Use this function to retrieve on which axis an “Any Motion” event was detected.
Syntax
uint8_t getAnyMotionSource();
Parameters
None.
Returns
The function returns a combination of any of these values:
MotionDetected: This flag indicates that a motion has been detected.
MotionOnX: This flag indicates that a motion has been detected on the X axis.
MotionNegativeX: This flag indicates that the motion on the X axis is a negative acceleration.
MotionOnY: This flag indicates that a motion has been detected on the Y axis.
MotionNegativeY: This flag indicates that the motion on the Y axis is a negative acceleration.
MotionOnZ: This flag indicates that a motion has been detected on the Z axis.
MotionNegativeZ: This flag indicates that the motion on the Z axis is a negative acceleration.
Example
void setup()
{
Motion.begin();
// Configure "Any Motion" to 1G during 500ms.
Motion.configAnyMotion(AxisAll, 1, 500);
}
void loop()
{
uint8_t any_motion;
any_motion = Motion.getAnyMotionSource();
if (any_motion & MotionDetected)
{
if (any_motion & MotionOnX)
{
// Process motion on X axis
}
if (any_motion & MotionOnY)
{
// Process motion on Y axis
}
if (any_motion & MotionOnZ)
{
// Process motion on Z axis
}
}
}
Motion.getTransientSource()
The Motion.getTransientSource function behaves just as the Motion.getAnyMotionSource() function but for “Transient” events. The function returns the same values.
See Motion.getAnyMotionSource().
Motion.getPulseSource()
Use this function to retrieve on which axis a “Pulse” event was detected.
Syntax
uint8_t getPulseSource();
Parameters
None.
Returns
The function returns a combination of any of these values:
- MotionPulseDetected: This flag indicates that a “Pulse” event has been detected.
- MotionPulseOnX: This flag indicates that a “Pulse” event has been detected on the X axis.
- MotionPulseNegativeX: This flag indicates that the “Pulse” event on the X axis has a negative acceleration.
- MotionPulseOnY: This flag indicates that a “Pulse” event has been detected on the Y axis.
- MotionPulseNegativeY: This flag indicates that the “Pulse” event on the Y axis has a negative acceleration.
- MotionPulseOnZ: This flag indicates that a “Pulse” event has been detected on the Z axis.
- MotionPulseNegativeZ: This flag indicates that the “Pulse” event on the Z axis has a negative acceleration.
- MotionDoublePulse: This flag indicates that a “Double Pulse” event has been detected.
Example
void setup()
{
Motion.begin();
// Configure "Pulse" to 1G during 50ms and 100ms latency
Motion.configPulse(AxisAll, 1, 50, 100);
}
void loop()
{
uint8_t pulse;
pulse = Motion.getPulseSource();
if (pulse & MotionPulseDetected)
{
if (pulse & MotionPulseOnX)
{
// Process pulse on X axis
}
if (pulse & MotionPulseOnY)
{
// Process pulse on Y axis
}
if (pulse & MotionPulseOnZ)
{
// Process pulse on Z axis
}
}
}
Motion.isEnabled
Use this function to know if the motion sensor is enabled.
Syntax
bool isEnabled();
Parameters
None.
Returns
Returns true if the sensor is enabled, false otherwise.
Motion.read (g)
Use this function to read the actual acceleration values from the sensor.
Syntax
bool read(float* x, float* y, float* z);
Parameters
The x parameter is a pointer to a float that will receive the current X axis acceleration value.
The y parameter is a pointer to a float that will receive the current Y axis acceleration value.
The z parameter is a pointer to a float that will receive the current Z axis acceleration value.
Returns
Returns true on success, false otherwise.
Example
void setup()
{
Motion.begin();
}
void loop()
{
float x, y, z;
if (Motion.read(&x, &y, &z))
{
// Process x, y and z
}
}
Motion.read (raw)
Use this function to read the actual axis register values (raw axis data) from the sensor.
Syntax
bool read(int16_t* x, int16_t* y, int16_t* z);
Parameters
The x parameter is a pointer to an unsigned 16-bit that will receive the current X axis raw value.
The y parameter is a pointer to an unsigned 16-bit that will receive the current Y axis raw value.
The z parameter is a pointer to an unsigned 16-bit that will receive the current Z axis raw value.
Returns
Returns true on success, false otherwise.
Example
void setup()
{
Motion.begin();
}
void loop()
{
int16_t x, y, z;
if (Motion.read(&x, &y, &z))
{
// Process x, y and z
}
}
Motion.readRegister
Use this function to read any register of the motion sensor.
Syntax
bool readRegister(uint8_t reg, uint8_t* value);
Parameters
The reg parameter is the register address to read. Refer to Addendum: registers definition.
The value parameter is a pointer to an unsigned 8-bit variable that will receive the register value.
Returns
Returns true on success, false otherwise.
Example
void setup()
{
uint8_t register;
Motion.begin();
// Read status register
Motion.readRegister(MMA8452_STATUS, ®ister);
}
Motion.writeRegister
Use this function to write to any register of the motion sensor.
Syntax
bool writeRegister(uint8_t reg, uint8_t value);
Parameters
The reg parameter is the register address to write. Refer to Addendum: registers definition.
The value paramter is the value to write.
Returns
Returns true on success, false otherwise.
Example
void setup()
{
uint8_t register;
Motion.begin();
// Read CTRL_REG1 register
Motion.readRegister(MMA8452_CTRL_REG1, ®ister);
// Write enable flag
Motion.writeRegister(MMA8452_CTRL_REG1, reg | 1);
}
Addendum: Registers definition
Here follows a list of constants with the definition of the registers you can use with the Motion.readRegister and Motion.writeRegister functions.
#define MMA8452_STATUS 0x00
#define MMA8452_OUT_X_MSB 0x01
#define MMA8452_OUT_X_LSB 0x02
#define MMA8452_OUT_Y_MSB 0x03
#define MMA8452_OUT_Y_LSB 0x04
#define MMA8452_OUT_Z_MSB 0x05
#define MMA8452_OUT_Z_LSB 0x06
#define MMA8452_SYSMOD 0x0B
#define MMA8452_INT_SOURCE 0x0C
#define MMA8452_WHO_AM_I 0x0D
#define MMA8452_XYZ_DATA_CFG 0x0E
#define MMA8452_HP_FILTER_CUTOFF 0x0F
#define MMA8452_PL_STATUS 0x10
#define MMA8452_PL_CFG 0x11
#define MMA8452_PL_COUNT 0x12
#define MMA8452_PL_BF_ZCOMP 0x13
#define MMA8452_P_L_THS_REG 0x14
#define MMA8452_FF_MT_CFG 0x15
#define MMA8452_FF_MT_SRC 0x16
#define MMA8452_FF_MT_THS 0x17
#define MMA8452_FF_MT_COUNT 0x18
#define MMA8452_TRANSIENT_CFG 0x1D
#define MMA8452_TRANSIENT_SRC 0x1E
#define MMA8452_TRANSIENT_THS 0x1F
#define MMA8452_TRANSIENT_COUNT 0x20
#define MMA8452_PULSE_CFG 0x21
#define MMA8452_PULSE_SRC 0x22
#define MMA8452_PULSE_THSX 0x23
#define MMA8452_PULSE_THSY 0x24
#define MMA8452_PULSE_THSZ 0x25
#define MMA8452_PULSE_TMLT 0x26
#define MMA8452_PULSE_LTCY 0x27
#define MMA8452_PULSE_WIND 0x28
#define MMA8452_ASLP_COUNT 0x29
#define MMA8452_CTRL_REG1 0x2A
#define MMA8452_CTRL_REG2 0x2B
#define MMA8452_CTRL_REG3 0x2C
#define MMA8452_CTRL_REG4 0x2D
#define MMA8452_CTRL_REG5 0x2E
#define MMA8452_OFF_X 0x2F
#define MMA8452_OFF_Y 0x30
#define MMA8452_OFF_Z 0x31


